 Reflections in Geometric optics:
Reflections in Geometric optics:
Reflection can be categorized into two types: diffuse reflection and specular reflection. To describe the gloss of the surface such as mirrors which has the property to simply reflect light in a predictable way, we use the Specular reflection. This helps n the formation of reflected images that can be categorized as extrapolated (virtual) or actual (real) images based on their location in space. Diffuse reflection is used to describe non-glossy surfaces such as rock or paper. Only statistically can describe the reflections from these surfaces using the exact distribution of reflected light which depends on the microscopic structure of the material. Lambert’s Cosine Law can be used to describe many diffuse reflectors. Lambert’s Cosine Law describes surfaces that have the same luminance when they are viewed from any angle. Glossy surfaces can give us both diffuse and Specular reflection.
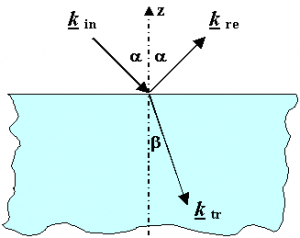
In specular reflection, the direction of the reflected ray is carried out with the help of the angle of incidence which the ray makes with the surface normal, which is a perpendicular line drawn from the point where the ray hits the surface. This whole phenomenon is known as the Law of Reflection.
In the case of flat mirrors, the law of reflection states that images of the object will be behind the mirror with the same distance as the object is from the mirror. Magnification is one that shows the size of the image and the size of the object is equal. This law also states that images produced by mirrors are parity inverted, which we observe as left-right inversion. Images that are formed from the reflection in two (or any multiple of two) mirrors are not parity inverted. Reflect rays are produced by corner reflectors that travel back in the same direction from which the incident ray came. This phenomenon is called retroreflection. For special purpose, precision optics and custom optical lenses are manufactured with the help of optical prism manufacturing process.
Curve mirrors
Mirrors that consist of curved surfaces can be constructed with the help of ray tracing and using the law of reflection at every point on the surface. Mirror those have parabolic or curved surfaces, when parallel rays fall on the surfaces of these mirrors they get reflected and tend to converge at a common focus point. Other curved surfaces can also focus light, but with divergence, the focus is blurred in space due to the aberration of shape. To be precise, spherical aberration is produced by spherical mirrors. Magnification of the images produced by the curved mirrors can be greater or less than one, and the magnification can be negative also which indicates that the image is inverted.